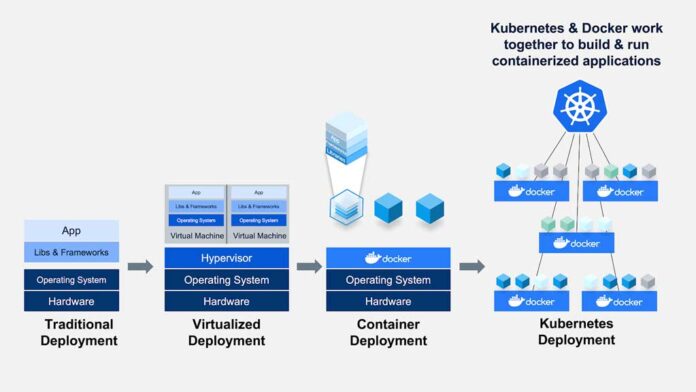
Docker and Kubernetes are complementary but serve different purposes in containerized application development and deployment. Here’s a detailed comparison:
1. Purpose
| Docker | Kubernetes |
|---|
| Docker is a platform for building, shipping, and running containers. It focuses on creating and managing individual containers. | Kubernetes is an orchestration tool for managing and scaling multiple containers across clusters of machines. |
2. Core Functionality
| Docker | Kubernetes |
|---|
| Provides tools to package applications and their dependencies into lightweight, portable containers. | Manages containerized applications across multiple nodes (servers), handling deployment, scaling, and failover. |
3. Role in the Ecosystem
| Docker | Kubernetes |
|---|
| Docker is responsible for creating containers and running them on a single host. | Kubernetes is responsible for orchestrating containers across multiple hosts and ensuring high availability. |
4. Scaling
| Docker | Kubernetes |
|---|
| Docker alone does not provide advanced scaling capabilities. You can manually start and stop containers or use Docker Swarm for basic orchestration. | Kubernetes excels at scaling, providing features like auto-scaling, load balancing, and rolling updates. |
5. Networking
| Docker | Kubernetes |
|---|
| Docker has a built-in networking model (bridge, overlay, host, etc.) but is limited to simpler setups. | Kubernetes offers a more advanced networking model with built-in support for service discovery, load balancing, and pod communication. |
6. High Availability
| Docker | Kubernetes |
|---|
| Docker alone does not manage high availability of containers. | Kubernetes ensures high availability by automatically restarting failed containers, replacing unhealthy nodes, and redistributing workloads. |
7. Multi-Node Support
| Docker | Kubernetes |
|---|
| Docker is designed to work primarily on a single node. Multi-node support is provided by Docker Swarm but is less advanced compared to Kubernetes. | Kubernetes is built for managing containerized applications across multi-node clusters by design. |
8. Storage
| Docker | Kubernetes |
|---|
| Docker supports mounting volumes for persistent storage but has limited advanced storage features. | Kubernetes provides advanced storage options like dynamic provisioning, persistent volumes (PVs), and persistent volume claims (PVCs). |
9. Ecosystem
| Docker | Kubernetes |
|---|
| Docker has its own ecosystem, including Docker Compose for managing multi-container applications on a single host and Docker Hub for sharing images. | Kubernetes has a vast ecosystem with tools like Helm (package manager), Kubectl (CLI), and integrations with monitoring, logging, and networking solutions. |
10. Learning Curve
| Docker | Kubernetes |
|---|
| Docker is relatively simple to learn and set up for small-scale applications. | Kubernetes has a steeper learning curve due to its complexity and the need to understand cluster management concepts. |
11. Dependencies
| Docker | Kubernetes |
|---|
| Docker is required to build and run containers, and Kubernetes often depends on Docker (or a container runtime like containerd or CRI-O). | Kubernetes uses Docker (or an alternative runtime) as the underlying container engine, but it focuses on orchestrating those containers. |
When to Use Docker vs. Kubernetes
-
Use Docker when you want to:
- Build and run individual containers or small-scale applications.
- Focus on development and local testing environments.
- Avoid the complexity of orchestration.
-
Use Kubernetes when you need to:
- Manage and orchestrate large-scale containerized applications.
- Ensure high availability, scalability, and fault tolerance.
- Work with multi-node clusters and automate deployments.
Can They Work Together?
Yes! Docker and Kubernetes are commonly used together:
- Docker is used to build and package containers.
- Kubernetes is used to orchestrate and manage those containers across clusters.
In modern setups, you might also see alternatives to Docker (like containerd or CRI-O) used as the container runtime with Kubernetes. However, Docker remains a popular tool for development and container creation.